EPO and Bodybuilding Performance: How Blood Oxygenation Affects Muscle Growth
If you're new to bodybuilding, you might think that improving your athletic performance relies on your nutrition, recovery, and the intensity of your workouts in the gym.
While nutrition, training intensity, and recovery are essential for improving performance, an equally important, but often overlooked, especially by beginners, element is blood oxygenation through EPO (erythropoietin).
Erythropoietin, or simply EPO, is used in medicine to treat anemia, particularly in patients with chemotherapy-induced anemia or chronic kidney failure. EPO helps these patients maintain healthy red blood cell counts despite their health conditions.
Bodybuilders and endurance athletes use EPO to boost their red blood cell production and thus improve oxygen delivery and performance in their bodies.
In terms of dosage, EPO is used by patients under strict medical supervision to prevent blood thickening and other complications that may occur.
However, although the use of EPO in the treatment of conditions such as anemia is approved by the FDA and completely legal, it should be noted that its use to improve endurance is deemed unethical by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). Therefore, if bodybuilders consider using EPO just before or during a competition, they can be arrested and suspended for doping.
In this guide, you'll learn the correlation between EPO and bodybuilding performance, as well as natural ways to increase EPO levels in bodybuilding.
What is erythropoietin and does EPO improve strength and endurance?
EPO (erythropoietin) is a natural hormone produced mainly by the kidneys when blood oxygen levels are below average.
EPO works by stimulating the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells (RBCs). RBCs are responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body, including vital organs and skeletal muscles. In other words, RBCs keep your entire body functioning properly.
High blood oxygen levels allow you to train harder and longer, as you experience less muscle fatigue during strength training sessions.
Additionally, the increased blood oxygenation throughout the body induced by EPO, which stimulates the bone marrow to produce more RBCs, can speed up recovery from your strength training sessions, while also improving nutrient delivery to skeletal muscles, nourishing them for optimal growth and performance.
So, does EPO improve strength and endurance?
Absolutely !
In summary, the correlation between EPO and bodybuilding performance is as follows:
#1. EPO improves endurance and stamina
As mentioned earlier, EPO is the hormone that tells the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells, which helps deliver more oxygenated blood to the entire body, including the skeletal muscle system.
The benefit to your performance is an increase in your endurance and stamina, as your muscles are not quickly overworked by muscle fatigue, which is responsible for the production of lactic acid during strength training.
Delaying muscle fatigue during strength training results in improved endurance and stamina, allowing you to perform more sets and reps on your exercises, ensuring intense, high-intensity workouts for optimal muscle gains and performance.
#2. Oxygen Optimization for Muscle Recovery
EPO ensures optimized oxygen delivery for muscle recovery by removing metabolic waste products, such as CO₂ and lactic acid, helping to reduce muscle discomfort, soreness, and pain.
Additionally, red blood cells transport essential nutrients like glucose and amino acids to muscle tissue, promoting much faster muscle repair during the recovery period. This is how blood oxygenation positively influences muscle growth.
It is also important to note that while oxygenation promotes optimal muscle recovery, some catabolism will persist during a long period of injury layoff or during the off-season.
#3. Increased muscle strength?
Oxygen is important for the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy source for muscles.
EPO increases the number of red blood cells, which results in better delivery of oxygenated blood to the muscles and, consequently, better availability of ATP.
This means your endurance is improved, which is ideal for progressive overload during strength training.
By practicing progressive overload during your strength training, you will gradually build muscle strength.
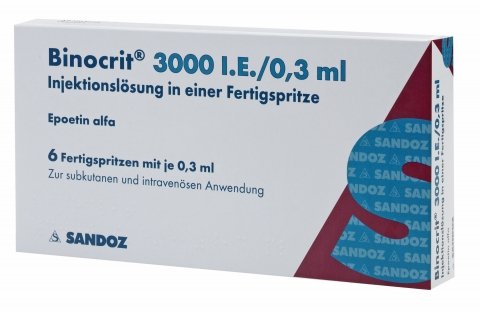
Recommended EPO Cycle and Dosages
All bodybuilders can use EPO. Here's a recommended cycle and dosage for beginners and intermediates.
Beginner bodybuilders
If you are new to bodybuilding, your EPO dosage should be 50 IU per kg of bodyweight.
You will be taking three (3) injections per week for two (2) weeks only. This dosage and cycle of EPO should be enough to significantly increase your red blood cell count and promote endurance gains.
Intermediate bodybuilders
For intermediate bodybuilders, your EPO dosage should be 100 IU per kg of bodyweight, injected three (3) times per week for two (2) weeks.
Note that EPO can be combined with other performance-enhancing substances (PAS) and/or anabolic steroids. However, it is advisable to consult an expert before using such a dosage.
Natural Methods to Increase EPO in Bodybuilding
It may be interesting to know that there are several natural methods for increasing EPO in bodybuilding. Some of the most common include:
Hypoxic or altitude training
You can naturally stimulate EPO production through hypoxic or altitude training, preferably at altitudes above 21,000 meters. This is why elite endurance athletes travel to countries like Colorado, Peru, and Kenya to train for major sporting events like marathons and cycling.
If you can't train at high altitude, you can simply wear a hypoxic mask in a controlled environment to simulate a low-oxygen environment and promote EPO production.
Consumption of iron-rich foods
Iron is a mineral essential for the production of red blood cells. If you're iron deficient, your body won't be able to efficiently transport oxygenated blood to all parts of your body, including vital organs and skeletal muscles. This leads to muscle fatigue and decreased strength training performance.
You can increase your iron intake through foods such as lentils, beans, lean red meat like bison and beef, fortified cereals, eggs, and dark leafy green vegetables like kale and spinach.
Use electrolytes and stay well hydrated
Did you know that when you're dehydrated, your blood thickens? This thickening makes it difficult for oxygen to circulate properly throughout your body.
Staying well hydrated at all times will ensure the proper functioning of your red blood cells, which circulate throughout your body with oxygenated blood.
Additionally, your body needs a good balance of fluids and electrolytes to ensure optimal oxygenation.
Potassium and sodium help improve fluid balance for the free movement of red blood cells, while magnesium promotes ATP production and calcium improves nerve transmission and greatly contributes to muscle contractions.
Cardio Training
Your cardio workout will go a long way toward optimizing your oxygenation. You can do either high-intensity interval training (HIIT), which will increase your overall oxygen uptake capacity, or low-intensity cardio (LISS), which will strengthen capillary density for optimal distribution of oxygenated blood throughout your body.
Supplementation
You can improve your EPO production and bodybuilding performance through supplementation. Beetroot extract, for example, can stimulate nitric oxide production and thus improve blood circulation.
Vitamins B6 and B12 are excellent for red blood cell production, and cordyceps is known to improve efficient oxygen utilization and VO2 max. Our experts offer you free advice on EPO and bodybuilding performance.
Conclusion
With of synthetic EPO and sound advice, you can quickly increase your red blood cell production and accelerate the distribution of oxygenated blood throughout your body to improve your athletic performance in record time.
Remember to maintain fluid balance through adequate electrolyte intake and hydration, while consuming iron-rich foods and supplements to improve red blood cell production and oxygenated blood flow, to build muscle strength and improve endurance. If possible, training in hypoxia or altitude can also stimulate EPO production and is highly recommended, especially if you are practicing endurance training.




Leave a Reply